Table of Contents
- Pre-Colonial Filipino Martial Arts Roots
- Colonial Influences
- American and Japanese Influences
- Modern Developments In Filipino Martial Arts
- Summary
“Filipino Martial Arts is a rich and diverse tapestry, woven from the threads of many different cultures and traditions. From the pre-colonial roots of indigenous Filipino martial arts, to the Spanish, Japanese, and American influences that have shaped it over the centuries, FMA is a testament to the resilience, adaptability, and creativity of the Filipino people.”
– Unknown
Filipino Martial Arts (FMA) is a highly diverse and dynamic martial arts system that has its roots in the Philippines.
Over the centuries, FMA has been shaped by a wide range of influences, including indigenous Filipino martial arts, Spanish colonialism, Japanese occupation, and American cultural influence.
Understanding the origins and influences of FMA is important not only for martial arts enthusiasts but also for anyone interested in the history and culture of the Philippines.
FMA is a reflection of the complex and fascinating history of the Philippines, with its blend of indigenous and foreign influences.
From its pre-colonial roots to its modern developments, FMA has been shaped by a wide variety of cultural and historical factors.
By exploring these influences, we can gain a deeper understanding of the rich and diverse tapestry that is FMA.
This blog post will delve into some of the key factors that have contributed to the evolution of FMA, highlighting the unique characteristics and techniques that make it one of the most distinctive and effective martial arts systems in the world.
Pre-Colonial Filipino Martial Arts Roots
Filipino Martial Arts (FMA) have deep roots in the pre-colonial indigenous cultures of the Philippines.
These martial arts traditions were developed as a means of self-defense and hunting, and were often tied to cultural and spiritual practices.
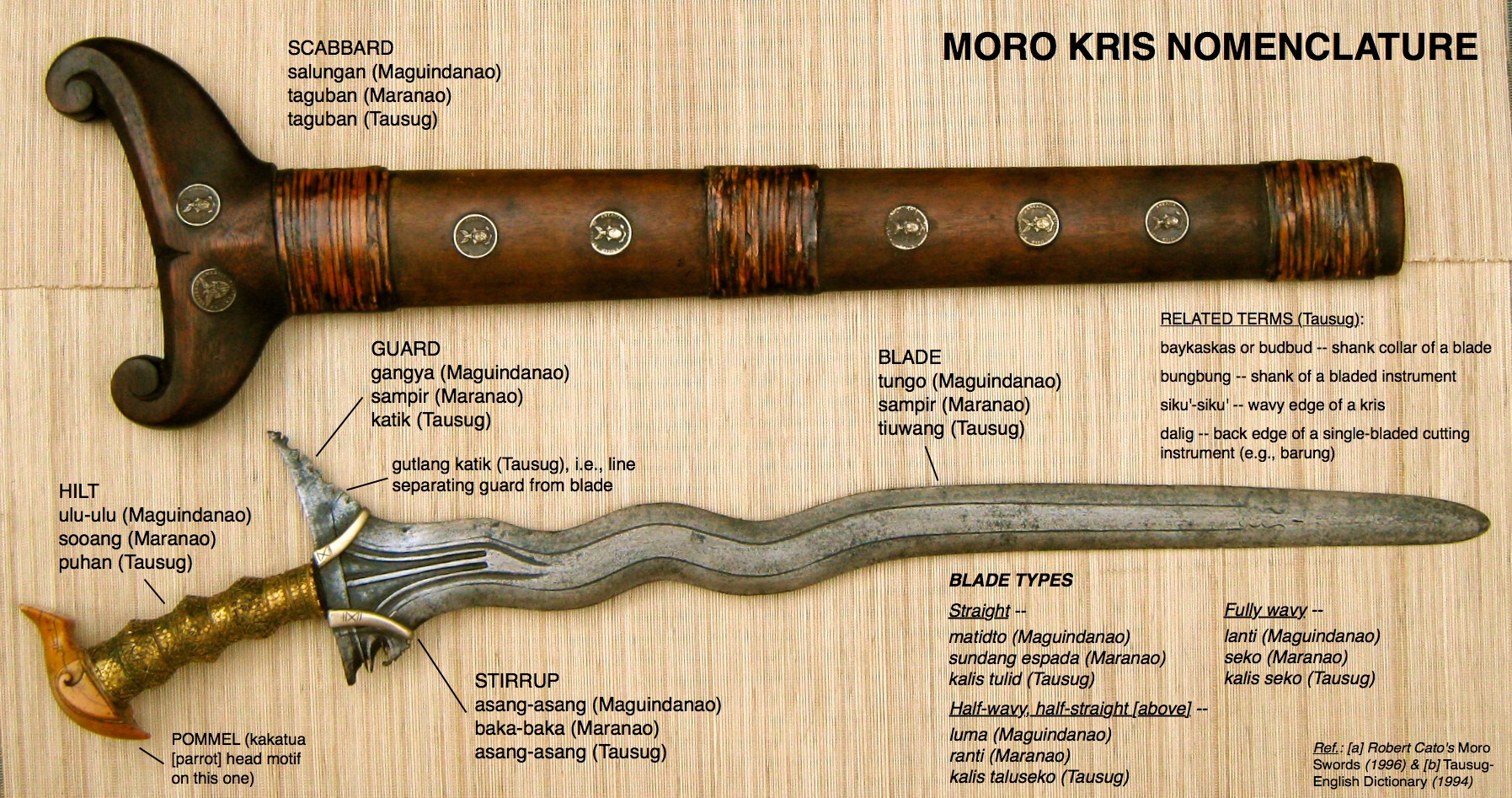
Pre-colonial FMA was characterized by a range of techniques and weapons, such as stick fighting, knife fighting, and empty-hand techniques.
These techniques were often used in combination with one another, creating a highly adaptable and versatile system of combat.
One of the most distinctive features of pre-colonial FMA was its emphasis on mobility and footwork.
This was due in part to the terrain of the Philippines, which includes dense forests, mountain ranges, and rugged coastlines.
Pre-colonial FMA practitioners had to be able to move quickly and efficiently over challenging terrain, making footwork an essential part of their training.
Another important aspect of pre-colonial FMA was its connection to cultural and spiritual practices.
Many FMA techniques were associated with specific deities or spirits, and were performed as part of religious or ceremonial rituals.
These practices were often passed down from generation to generation through oral tradition, with elders passing on their knowledge and wisdom to younger members of the community.
Despite the diverse range of techniques and practices associated with pre-colonial FMA, there were also commonalities between different styles and regions.
These commonalities included an emphasis on practicality and effectiveness, as well as a respect for tradition and cultural heritage.
Many modern FMA styles still draw on the pre-colonial roots of the art, incorporating techniques and principles from these early traditions.
By studying and understanding the pre-colonial origins of FMA, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the cultural and historical significance of this martial arts system.
Colonial Influences
The colonial period in the Philippines, which lasted for more than three centuries, had a significant impact on the development of Filipino Martial Arts (FMA).
During this time, the Philippines was under Spanish rule, and Spanish martial arts had a profound influence on FMA.
Spanish martial arts, which included techniques such as the rapier and dagger, were introduced to the Philippines by the Spanish conquistadors.
These techniques were quickly adopted and adapted by Filipino martial artists, who incorporated them into their own systems of combat.
The result was a hybrid system of martial arts that combined Spanish and indigenous techniques, creating a unique and highly effective martial arts style.
One of the most distinctive features of Spanish-influenced FMA was its use of bladed weapons, such as the sword and the knife.
These weapons were used in combination with empty-hand techniques, creating a versatile and deadly system of combat.
Spanish-influenced FMA also emphasized the use of angles and footwork, allowing practitioners to move quickly and efficiently in combat.
The Japanese occupation of the Philippines during World War II also had a significant impact on FMA.
During this time, Japanese martial arts such as Judo, Karate, and Aikido were introduced to the Philippines, and many FMA practitioners began to incorporate these techniques into their own training.
The result was a further evolution of FMA, with practitioners combining techniques and principles from different martial arts traditions to create a highly adaptive and effective system of combat.
This hybrid system of martial arts has continued to evolve in the modern era, with practitioners drawing on a wide range of influences and techniques to create new and innovative styles of FMA.
FMA remains deeply rooted in the cultural and historical traditions of the Philippines, while also incorporating techniques and principles from other martial arts traditions.
By studying the colonial influences on FMA, we can gain a deeper understanding of the art’s evolution and the cultural and historical factors that have shaped it over time.
American and Japanese Influences
The period of American and Japanese occupation in the Philippines had a significant impact on the development of Filipino Martial Arts (FMA).
During this time, FMA practitioners were exposed to a wide range of new martial arts techniques and styles, which contributed to the evolution of FMA into a hybrid system that drew on a diverse range of influences.
Japanese martial arts such as Judo, Karate, and Aikido were particularly influential during this time.
Japanese martial arts were introduced to the Philippines during World War II, when the Japanese occupied the country.
Many FMA practitioners began to study and incorporate Japanese techniques into their own training, resulting in the development of hybrid martial arts systems that combined Japanese and Filipino techniques.
One of the most significant contributions of Japanese martial arts to FMA was the emphasis on discipline and formalized training methods.
Japanese martial arts introduced a more structured and regimented approach to martial arts training, which helped to standardize and systematize FMA training methods.
American boxing also had a significant influence on FMA during this time.
The sport of boxing was introduced to the Philippines during the American occupation, and many FMA practitioners began to incorporate boxing techniques into their own training.
American boxing emphasized footwork, timing, and speed, which were all important aspects of FMA as well.
Incorporating boxing techniques into FMA helped to make the art more accessible to a wider audience, as it provided a more familiar and recognizable framework for training.
It also helped to establish FMA as a practical system of self-defense that was effective against a range of different combat styles and techniques.
FMA continues to evolve and incorporate new influences from around the world.
While the art remains deeply rooted in Filipino culture and history, it has become a global phenomenon that draws on a diverse range of techniques and practices.
By studying the American and Japanese influences on FMA, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the art’s evolution and its significance in the wider world of martial arts.
Modern Developments In Filipino Martial Arts
In the modern era, Filipino Martial Arts (FMA) has continued to evolve and develop, incorporating new influences and techniques from around the world.
FMA has become a global phenomenon, with practitioners and enthusiasts from all corners of the globe.
One of the most significant modern developments in FMA has been the emergence of new styles and techniques.
Over the years, FMA has evolved into a hybrid system that incorporates techniques and principles from a wide range of martial arts traditions.
This has led to the development of new and innovative styles of FMA, each with its own unique characteristics and training methods.
Many modern FMA styles place a greater emphasis on practical self-defense techniques, as well as on physical fitness and conditioning.
This has led to the development of new training methods and approaches, such as strength and conditioning programs and specialized training for specific combat scenarios.
In addition, FMA has become increasingly popular as a sport, with many competitions and tournaments held around the world.
These competitions showcase the skills and techniques of FMA practitioners, and provide an opportunity for enthusiasts to connect and share their love of the art.
The global spread of FMA has also led to a greater appreciation and recognition of the art’s cultural and historical significance.
Many FMA practitioners today seek to preserve and promote the art’s rich cultural heritage, while also adapting it to meet the needs of modern practitioners and society.
Overall, the modern era has seen FMA evolve and adapt to the changing needs and demands of the world.
While the art remains deeply rooted in Filipino culture and history, it has become a truly global phenomenon that draws on a wide range of influences and traditions.
Summary
Filipino Martial Arts (FMA) is a highly diverse and dynamic martial arts system that has its roots in the Philippines.
FMA has been shaped by a wide range of influences, including indigenous Filipino martial arts, Spanish colonialism, Japanese occupation, and American cultural influence.
Pre-colonial FMA was characterized by a range of techniques and weapons, such as stick fighting, knife fighting, and empty-hand techniques.
These techniques were often used in combination with one another, creating a highly adaptable and versatile system of combat.
During the Spanish colonial period, Spanish martial arts such as the rapier and dagger were introduced to the Philippines, and were quickly adopted and adapted by Filipino martial artists.
The result was a hybrid system of martial arts that combined Spanish and indigenous techniques, creating a unique and highly effective martial arts style.
During World War II, the Japanese occupation of the Philippines had a significant impact on FMA.
Japanese martial arts such as Judo, Karate, and Aikido were introduced to the Philippines, and many FMA practitioners began to incorporate these techniques into their own training.
The period of American and Japanese occupation in the Philippines had a significant impact on the development of FMA, as FMA practitioners were exposed to a wide range of new martial arts techniques and styles.
American boxing also had a significant influence on FMA during this time.
In the modern era, FMA has continued to evolve and develop, incorporating new influences and techniques from around the world.
The emergence of new styles and techniques, as well as the global spread of FMA, has led to a greater appreciation and recognition of the art’s cultural and historical significance.
Overall, the history of FMA is a reflection of the complex and fascinating history of the Philippines, with its blend of indigenous and foreign influences.
FMA remains deeply rooted in Filipino culture and heritage, while also incorporating techniques and principles from other martial arts traditions.
By studying and understanding the history of FMA, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the art’s evolution and the cultural and historical factors that have shaped it over time.
Additional Resources
- FMA Digest – This website is a comprehensive resource for all things related to Filipino Martial Arts, including news, reviews, and articles about the latest trends and techniques in the field. It also features a directory of FMA schools and instructors around the world.
- Global FMA Network – This website provides a global network of FMA practitioners and enthusiasts, offering a platform for sharing knowledge, insights, and experiences. It also hosts an online forum for discussion and debate about the latest trends and developments in the field.
- FMA Pulse – This online magazine features in-depth articles, interviews, and videos about Filipino Martial Arts, covering a wide range of topics from technique to culture and history. It is a great resource for anyone interested in exploring the many facets of FMA.